Error message title

Error message title
Searching great energy plans for you
What is hydrogen?
Hydrogen is a lightweight gas found in water and hydrocarbons (such as oil and natural gas). It’s the most abundant element in the universe.
Why is there so much buzz around hydrogen?
There is more and more interest in hydrogen because of the way it unlocks the potential of other renewable power sources. Companies like ENGIE are working hard to find ways to make hydrogen power a viable ongoing source of energy.
How does hydrogen unlock the potential of renewable energy?
Hydrogen is great because it allows us to store the excess energy created by wind and solar power when it’s windy and sunny, for use it when it’s not. It allows a constant supply of these weather-dependent renewable resources.
How is green hydrogen made?
Green hydrogen can be produced when the supply of renewable energy sources is greater than its demand. The surplus electrical current is passed through water which causes it to split into (H2) and Oxygen (O2) through a process called electrolysis. How is green hydrogen used? The hydrogen produced during electrolysis can be stored or transported. It can be used directly (particularly as a fuel), injected into the natural gas supply network, or converted back to electricity by combining it with oxygen in a fuel cell. It can be used to power cars, buses, homes, businesses, industries and cities. Hydrogen can smooth out renewable electricity production. This makes it a viable long-term replacement for carbon emitting energy alternatives.
Pros
| Cons
|
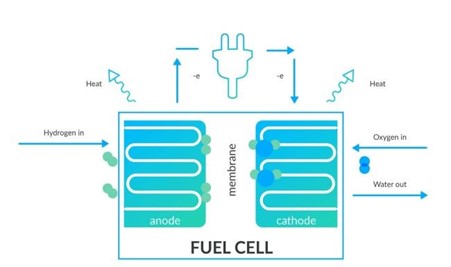
How does a hydrogen fuel cell work?
Although hydrogen is abundant in water, the hydrogen atom which is used to make electricity must be produced.
This can be done through a process called steam reforming, but this method produces carbon dioxide, the very thing we are trying to avoid.
Fuel cells are the green option. They are devices that generate electrical power by chemical reaction. They are very efficient and clean – their only by-products being electricity, heat, and water.
A fuel cell is made up of an anode, a cathode and an electrolyte membrane.
The hydrogen travels through the anode of a fuel cell and oxygen goes through the cathode.
At the anode, the hydrogen is split into electrons and protons.
The protons move through the electrolyte membrane, while the electrons travel through a circuit, generating an electric current and excess heat.
At the cathode, the protons, electrons, and oxygen combine to produce water molecules.